Apache Tomcat 8.5 Download
Apache Tomcat, free download. Apache Tomcat 8.0.53: Apache Tomcat is a web server that is an open source software implementation of the Java Servlet and JavaServer Pages technologies. 1,746,000 recognized programs - 5,228,000 known versions - Software News.
- Download Apache Tomcat - Java servlet Internet server formerly also Jakarta Tomcat that provides a. DOWNLOAD Apache Tomcat 9.0.41 / 8.5.61 / 7.0.107 / 10.0.0-M9 Alpha for Windows.
- Tomcat 8.5 was designed to run on Java 7 or later. Binary downloads of the Tomcat server are available from https. The Apache Software Foundation.
- 🅳🅾🆆🅽🅻🅾🅰🅳 Free download Apache Tomcat 8.5.12/9.0.0 M19 (alpha) Java servlet Internet server formerly also Jakarta Tomcat that provides a 'pure Java' HTTP web server environment for Java code to run in. Read more about Apache Tomcat.
Latest Version:
Requirements:
Windows XP / Vista / Windows 7 / Windows 8 / Windows 10
Author / Product:
Apache Software Foundation / Apache Tomcat
Old Versions:
Filename:
apache-tomcat-8.5.50.exe
Features and Highlights
- Deployer - Operating the Tomcat Deployer to deploy, precompile, and validate web applications.
- Manager - Operating the Manager web app to deploy, undeploy, and redeploy applications while the app is running.
- Host Manager - Operating the Host Manager web app to add and remove virtual hosts while the app is running.
- Realms and Access Control - Description of how to configure Realms (databases of users, passwords, and their associated roles) for use in web applications that utilize Container Managed Security.
- Security Manager - Configuring and using a Java Security Manager to support fine-grained control over the behavior of your web applications.
- JNDI Resources - Configuring standard and custom resources in the JNDI naming context that is provided to each web application.
- JDBC DataSource - Configuring a JNDI DataSource with a DB connection pool. Examples for many popular databases.
- Classloading - Information about class loading in the software, including where to place your application classes so that they are visible.
- JSPs - Information about Jasper configuration, as well as the JSP compiler usage.
- SSL/TLS - Installing and configuring SSL/TLS support so that your Tomcat will serve requests using the https protocol.
- SSI - Using Server Side Includes in the app.
- CGI - Using CGIs with the app.
- Proxy Support - Configuring the app to run behind a proxy server (or a web server functioning as a proxy server).
- MBeans Descriptors - Configuring MBean descriptors files for custom components.
- Default Servlet - Configuring the default servlet and customizing directory listings.
- The Clustering - Enable session replication in the environment.
- Balancer - Configuring, using, and extending the load balancer application.
- Connectors - Connectors available in the app, and native web server integration.
- Monitoring and Management - Enabling JMX Remote support, and using tools to monitor and manage Apache Tomcat.
- Logging - Configuring logging in the software.
- Apache Portable Runtime - Using APR to provide superior performance, scalability, and better integration with native server technologies.
- Virtual Hosting - Configuring virtual hosting in Tomcat.
- Advanced IO - Extensions available over regular, blocking IO.
- Additional Components - Obtaining additional, optional components.
- Using the libraries with Maven - Obtaining Tomcat jars through Maven.
- Security Considerations - Options to consider when securing an installation.
- Windows Service - Running the program as a service on Microsoft Windows.
- Windows Authentication - Configuring the app to use integrated Windows authentication.
- High Concurrency JDBC Pool - Configuring the app to use an alternative JDBC pool.
- WebSocket support - Developing WebSocket applications for Tomcat.
- URL rewrite - Using the regexp based rewrite valve for conditional URL and host rewrite.
- CDI and JAX-RS support - Configuring CDI, JAX-RS, and Eclipse Microprofile support.
Note: Requires Java Runtime Environment.
This brief tutorial shows you how to get Tomcat version 8 series ( 8.5) on Ubuntu 16.04 18.04 LTS systems. If you don’t know what Tomcat is, here’s an overview…
Apache Tomcat software is an open source implementation of the Java Servlet, JavaServer Pages, Java Expression Language and Java WebSocket developed by the Apache Software Foundation… Although not as popular as Apache2 or Nginx HTTP servers, Tomcat is still important to some projects…
Tomcat works best when rendering web pages the include Java server page coding and Java Servlet… These languages are still required by some other protocols used by Java developers.
This brief tutorial is going to show students and new users how to install Tomcat on Ubuntu 16.04 18.04…
When you’re ready to install Tomcat, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Install OpenJDK
Tomcat requires Java JDK to be installed in order to function… You can either install Oracle Java JDK or its open source alternative called OpenJDK.
For this tutorial, we’re going to be installing OpenJDK and to install it in Ubuntu is pretty straightforward…
Simply run the commands below to install OpenJDK:
That should install OpenJDK 8 and configure it as the default…
Apache Tomcat 8.5 Download 64 Bit
Now that Java is installed, we can now download and create a tomcat user, which will be used to run the Tomcat service.
Step 2: Create Tomcat Service Account
You’ll want to run Tomcat as it own user without root privileges… You should create a new user and group that will run the Tomcat service… To do that, run the commands below
First, create a new tomcat group called tomcat. Linux systems usually create groups based on the account name.
sudo groupadd tomcat
Next, create a new tomcat user called tomcat and make the user a member of the tomcat group above…. To do that, run the commands below
sudo useradd -s /bin/false -g tomcat -d /opt/tomcat tomcat
Now that our tomcat user is set up, let’s download and install Tomcat package.
Step 3: Download Tomcat Packages
After installing OpenJDK and creating a service account for Tomcat, run the commands below to download Tomcat version 8. At the time of this writing the latest version of the 8 series was 8.5.42.
You can get the latest from the link below:
After downloading, we’ll also want to create a new Tomcat directory at /opt/tomcat. Then we’ll extract the downloaded content into that directory…
To do that, run the commands below:
Next, give the tomcat user control of the entire directory and make all the scripts in the bin location executable…
When you’re done, continue below to creating Tomcat service…
Step 4: Configure Tomcat Service
Now that the package is extracted, run the commands to open Tomcat configuration file for its default user
sudo nano /opt/tomcat/conf/tomcat-users.xml
Then create an account with password for the user and save by copying and pasting the lines below into the file. just before the </tomcat-users>
Save the file and exit.
Next, run the commands below to create a server account for Tomcat
Apache Tomcat 8.5 Download
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
then copy and paste the lines below into the file and save
Save and exit.
After that, run the commands below to reload systemd profiles and enable tomcat service…
To check if Tomcat is running or not, run the commands below:
sudo systemctl status tomcat.service
You should get similar screen as below;
That is how you now tomcat is running…
Now, open your browser and browse to the local server IP or hostname
and you should see Tomcat default page.
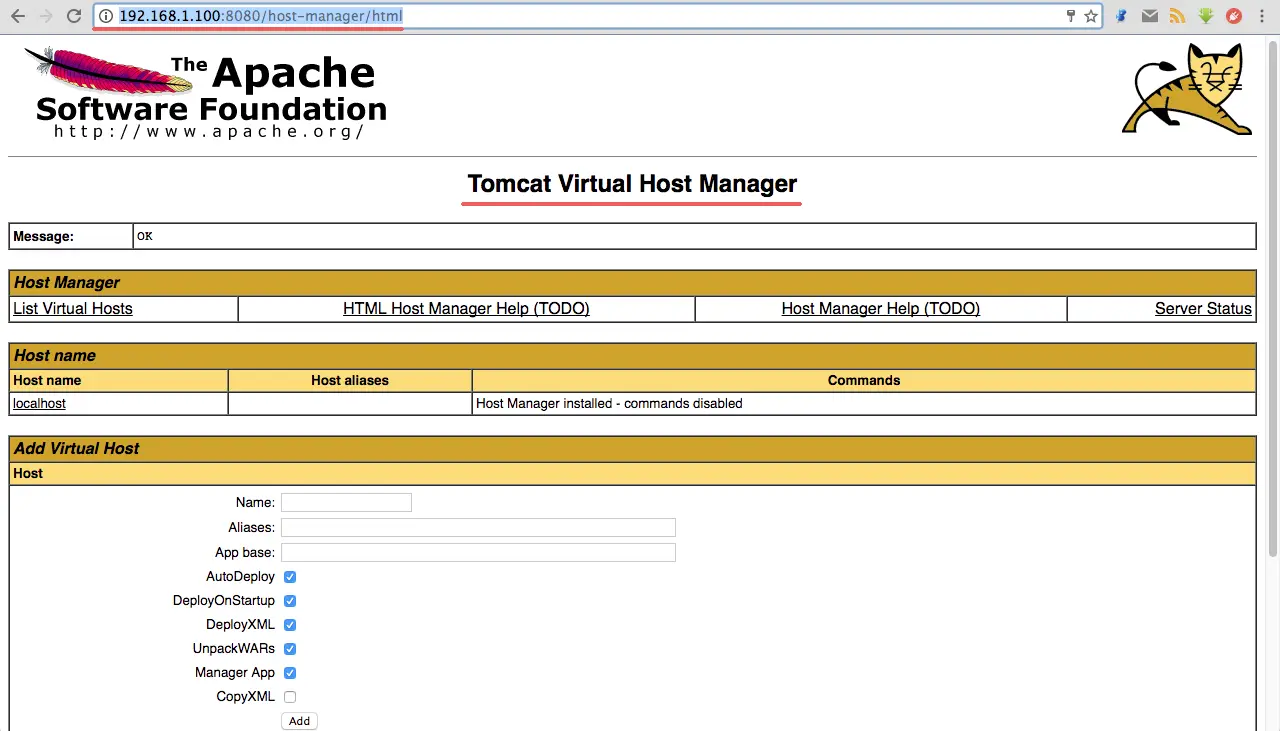
Click on the Manager App to logon to the backend page…
By default,Tomcat restrict access to the Manager and Host Manager apps to connections coming the local server only… If you want to access the Tomcat server remotely, you’ll want to whitelist the remote IP address to be allowed… To change the IP address restrictions on these, open the appropriate context.xml files.
For the Manager app, type:
How to update cracked serum. sudo nano /opt/tomcat/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml
For the Host Manager app, type:
sudo nano /opt/tomcat/webapps/host-manager/META-INF/context.xml
Inside, comment out the IP address restriction to allow connections from anywhere. Alternatively, if you would like to allow access only to connections coming from your own IP address, you can add your public IP address to the list:
Save and close the files and you’re done!
That’s it!
Congratulations! You have successfully installed and configured Tomcat 8 8.5 on Ubuntu 16.04 and 18.04 LTS systems.
You may also like the post below: